Monday, July 4, 2011
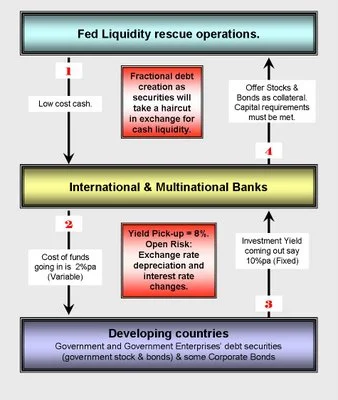
The Operations "carry trade" Part-1
The port - or carry trade - is a relatively simple operation which is to take advantage of a gap in performance between asset classes: asset borrowed at low rates are placed in high-yield assets. Today, the phenomenon has grown strongly on the yen, becoming problematic. that evidenced by recent calls from the President of the Eurogroup, Jean-Claude Juncker, and many analysts, asking the President of the Bank of Japan to reconsider its policy. They do not seem to find echoes in Japan, but show an awareness of the danger generated. However, failure to report the problem exists at the conference of the G8 does not seem to be in line for a quick response.
The carry trade exchange, a concept theoretically unworkable in the long term. A currency carry trade involves borrowing in a currency in a country where rates are low, to change the money into a currency "strong" and place it high (treasuries ...). Theoretically, the operation of the arbitration process is ephemeral because the markets are efficient (at each moment is a financial security to its price) and rebalance through exchange rates and interest rates.
In addition, because of the rule of parity uncovered interest rate, the interest of such an operation is theoretically zero. Indeed, a difference in rates between two countries reflects inflation differentials. But these differences are offset by a realignment of exchange rates. Thus, when an investor speculates on the difference in rates observed between the two countries, he loses the same value on the exchange. That said, sometimes the law does not hold in practice and that the currencies of countries with low rates and suffer the opposite effect depreciate. This is the case of the yen, which reached historic lows against the U.S. dollar and the euro.
Friday, July 1, 2011
The quality indicators
Quality indicators of user processes (Drivers main directions of the risks, liabilities, financial, marketing, commercial)
As part of the approval process with Basel 2 instances of trust, quality indicators should focus mainly on:
* The validity of the SI risk management
* The performance score of grant, the organization of the rating systems and delegation
* Compliance with the risk strategy in terms of authorization and action limits
These include examples of indicators as the rate of customer doubtful with a healthy note, the rate of third unrated or with a note too old, or the rate of others rated their group.
To control effectively the quality of each indicator, it is essential to have previously defined a responsible business and responsible SI (the MOA) on each of the data information system.
The process of defining indicators is iterative, since the priorities may change based on improvements. To control them properly, it is preferable to retain only 10 in the first place. The dashboard can be enriched progressively as the process will be better understood by employees and more mature. For an effective control, must not exceed twenty indicators, which requires the definition of an arbitration process indicator to be adopted.
Once the dashboard as defined with the various indicators chosen, it must be operated and monitored on a recurring basis. Identified as significant variables of a state, the indicators need to restore an image quality of the management of risks by focusing on the area’s most sensitive to the context and business goals. As a minimum, an annual review to define the quality policy to hold, but the quality is a daily challenge; do not forget to make some adjustments over the water...
Labels:
commercial,
financial,
marketing,
quality indicators,
SI risk management
Definition of Indicators
The definition of indicators based on the combination of an empirical, research-based elements of non-quality in the device in place, and a theoretical approach, having as a starting point to identify key parameters management customer risk:
To invest in the improvement actions that correct the non-quality aspects of the most sensitive, the first step is to build a balanced scorecard indicators are most representative. It is an indispensable asset to the achievement of a critical diagnosis and appropriate vis-à-vis business strategies (risk, marketing, sales ...) defined. While some indicators can be retained only for statistical purposes, the others must be action-oriented: this means they must be involved in a lens quality (which will result in the definition of alert thresholds or levels of expected results ...) and an action plan to achieve the objective. The role of each business direction and / or SI concerned to arrive at the expected level of quality must be so in a charter previously defined: it is one of the key success factors of the process.
Identify the characteristics of the third party repository brings out the different types of people (customers, prospects, guarantees ...), information (customer classification, signs of third party monitoring bodies ...), for which the required quality levels are not necessarily the same. Two examples: the rate of duplication, including the reduction can improve the consolidation process and risk capital allocation, the rate of third parties not identified as an affiliate of the bank, resulting in poor consolidation risk on intra banking group.
Wednesday, June 29, 2011
Reliability Of Shares

Shares of reliability, often initiated by the trades and in consultation with the project owners, are intended to identify areas of non-quality, identify the causes and identify pragmatic ways to mitigate or delete.
The first actions are almost always in the form of manual corrections. These projects mobilize substantial charges to align the repository with the reality-duplication, enhancement or correction of signs, etc ... In addition, these actions if they can have a satisfactory short-term, must be renewed frequently to maintain quality and fight against the progressive drift.
In the long run, it is best to think of more sustainable solutions and, in this regard, the levers are very diverse appointment of quality managers in the contributing entities, workflow validation of customer data, standardization of concepts , comparisons with external sources, management of several criteria of uniqueness ... The possible solutions are many but their cost, period of implementation and impact on data quality is variable. However, the prioritization of these actions is often subjective: some effects more "visible" are given priority while others are ignored because their quality impacts are unknown.
The success of the business plan requires a continuous improvement in performance. It should be laid down in processes that involve the third party repository, a real cornerstone of the IF bank. Based on the quality approaches used in industry (six-sigma, Total Quality Management ...), the virtuous cycle is divided into five phases: definition of indicators and quality objectives of the standard, indicators measuring, analyzing results, identifying actions to improve the quality control of the effect of implemented solutions. We propose in this article, to limit ourselves to the first two phases that we consider most important.
Operative management - data quality
The importance of data quality in the operative management of counterparty risk.
Despite the efforts made by financial institutions to ensure compliance with the Basel 2, the internal audits and supervisory bodies highlight gaps in devices management customer risk.
Beyond the third scoring models in place to comply with regulations, financial institutions must continue efforts to ensure a sustainable level of quality control and so effectively and Reliable customer risk. If there are relatively simple and fast to improve data quality, only a comprehensive approach and equipped keeps this level over time and create a culture of quality in financial services, with the image of the industry.
The banking and financial regulation on the internal control of credit institutions and investment firms provides an outline of points to watch it should be integrated within the device management of counterparty risk.
To ensure compliance with regulations and ensure the proper level of control internally, branches wish to have the core quality indicators ensuring the validity of the information system risk management, validating the defined risk strategy and organization established to cover the risk client. The only way to dispose of is to use information systems to provide a quantitative analysis, but the relevance of these indicators is based on the quality of the IS.
System-level information, the presence of duplicates, unreliable links or combinations obsolescence of client identification are some examples of non-referential quality of the third most frequently cited. If they do not prevent the IF function, these problems can have a significant impact on end users and in particular the process of consolidating risks, commercial pilot, the fight against money laundering and grant decisions.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)